What are OPGWs/OPPCs?
OPGW stands for ‘Optical Ground Wire,’ which is used in overhead power lines for grounding and communication. OPPC stands for ‘Optical Phase Conductor,’ and it’s a cable with the function of phase and communication in the system. OPGW and OPPC are primarily used in the energy industry. OPGW and OPPC provide telecommunication paths for internal and third-party communications.
In addition to telecommunications, optical fiber can alert a control center of any changes to the temperature by using Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS), providing operators with precise real-time information on the behavior and condition of the line. Having access to real-time temperature data is vital in OPPC lines. Operators can streamline more power through a given branch when the temperature is within the operational limit, effectively creating a “smart” grid.
PBT Loose Tube and FIMT are two separate fiber optic constructions that are integratable within ground wire and phase conductors. This post will explore the design and properties of each cable to provide a comprehensive breakdown and determine which solution performs better in the field.
What is PBT Loose Tube?
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is a standout material for high-end engineering applications due to its excellent stain resistance, machining characteristics, and excellent short-term mechanical properties, such as high strength, toughness, and stiffness. It provides good creep resistance, dimensional stability, and low moisture absorption characteristics. The properties of PBT experience little change even in high-temperature and moist environments, making it a suitable material for high-voltage environments, such as power lines.
PBT Loose Tube is designed to perform in outdoor conditions, aerial, duct, and direct-buried applications. A gel is also positioned within the tube with the optical fibers underneath the protective layers. As the fibers are ‘loose’ inside the protective jacket, they are more immune to the effects of outside forces.
What is FIMT?
In contrast to PBT Loose Tube, FIMT replaces the PBT layer of protection with a metal layer that shields the optical fiber. There are countless possible configurations of FIMT, but the basic setup is a steel strip, gel, optical fibers. Optionally an additional outer aluminum layer can be added to protect against environmental influences and prevent issues such as galvanic corrosion for example.
FIMT can be produced with various protective metal tubes differing in alloys, steel grades, and thickness. Additional metal layers, stranding wire, and extra cladding can also be included in the construction. Finally, hundreds of high-performance polymer options can be added to provide additional outer layers for extra protection in challenging conditions. In total, there are over 80,000 possible configurations, including the following three popular OPGW/OPPC examples:
Single Layer FIMT
Single layer FIMT is commonly used for stranded layered structured OPGWs or OPPCs. The tube is filled with a thixotropic gel to further protect the fibers from water ingress, locking the fibers inside the tube. The ultra-small form factor enables easy integration into bigger assemblies by replacing single stranding wires without compromising the mechanical properties. Most common designs use up to three FIMTs in a cable with a maximum of 192 fibers (200μm OD) per FIMT. Different sizes, amounts of fibers, materials, and gels can be chosen by our customers, ensuring the best fit of our FIMTs for your OPGW / OPPC project. For stranded layered structures, Single Layer FIMT is the perfect choice as it provides the smallest form-factor. In such a structure, the FIMT replaces single stranding wires. The de-centralized position helps to reduce strain on the fibers, which allows for increase sag caused by excessive load.
Thin wall aluminum FIMT
Thin Wall Aluminum Layered FIMT is especially suitable for small-form-factor cables. It combines the benefits of high crush and kink resistance with small size while still preventing galvanic corrosion, making it a perfect choice for lightweight cable designs within harsh environments. In addition, the added aluminum layer eliminates the necessity of grease during production, allowing for easy assembly for our customers by only adding additional stranding layers.
Thick Wall Aluminum Layered FIMT
Thick Wall Aluminum Layered FIMT offers the best crush and kink-resistant properties. In addition, the aluminum helps increase fault current performance and reduces the necessary amount of Aluminum Alloy Stranding Wires. The fibers are assembled as a loose tube construction in the metal tube filled with a thixotropic gel to prevent water ingress and secure the excess fiber length. The customer can choose the amount and types of fibers, inner tube material, and gel. In addition, the aluminum layer adds to the overall cross conductor section, which helps to increase fault current performance and reduce the necessary amount of Aluminum Alloy Stranding Wires. Therefore, more and heavier aluminum cladded wires can be used making this FIMT especially suitable for OPGWs with long distances between power poles. Characteristics such as outer diameter, wall thickness, amount and type of fibers and various materials can be selected based on customer demand, offering highest level of flexibility and always tailored cable solutions for best fit approach.
NBG recently contributed 88 km of FIMT for the EVN project between Gmünd and Groß Gerungs. Our robust tubes protect the optical fiber from environmental influences such as lightning, guaranteeing high performance and reliability for the entire area.
FIMT vs. PBT Loose Tube cables for OPGW
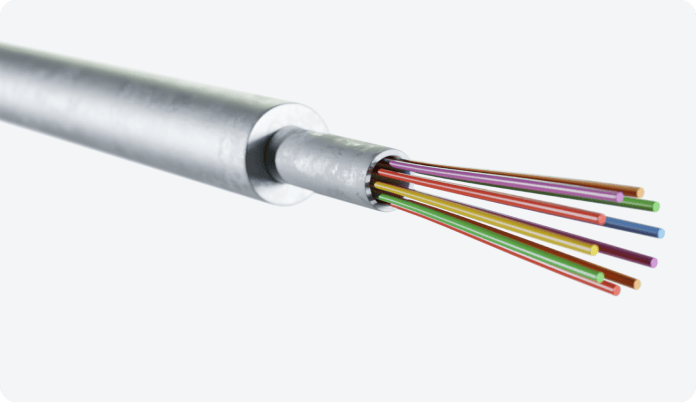
One advantage of the PBT Loose Tube construction is that ‘Fiber Differentiation’ is more straightforward. In FIMT designs, fibers can be differentiated by the fiber color itself, by additional ring markings with different codes, and by bundling multiple fibers with colored yarns. Fiber differentiation is part of the design process of FIMT and a wide range of options are available. Although a PBT Loose Tube is lighter, FIMT offers more flexibility in design and higher fiber density can balance the heavier weight of the FIMT.
In conclusion, FIMT provides ground wires the best protection against lightning strikes and other external influences, ensuring the long-term reliability of the network and a better return on investment.



